What is EQ in Music? | EQ EXPLAINED (2022)

“So what is EQ in music?”
EQ or “equalisation” is an incredibly powerful musical tool that can be used to shape the frequency response of a sound.
Our ears can detect a huge range of frequencies—approximately 20 Hz to 20 kHz. EQ can be use to sculpt this frequency range, which changes the tone and character of the EQ’d sound.
In other words, it is the process of adjusting the gain of specific frequency ranges of a sound. For example, if you have a sound with quiet bass frequencies, you can use EQ to increase the low-end frequencies to add more bass to the sound. Similarly if the bass is too loud, EQ can be used to decrease (or even completely remove) the bass frequencies.
When would I need EQ in music?
EQ in music is particularly important during the mixing process of a track. For example, EQ can be used to identify and remove any harsh, resonant frequencies that may be ruining the mix. It can also be used to ensure that various instruments / sounds aren’t all occupying the same frequencies, which can make a track sound “muffled” and unprofessional.
If you’re a music production beginner, it’s crucial you understand the fundamentals of EQ in music. EQ will become one of your most commonly used mixing tools, so it’s important you get your head around the basics.
EQ in Music – How to start using EQ in your tracks
You can start using EQ by loading an EQ VST plugin inside your DAW. You can also control EQ via hardware, but virtually all modern producers use VST plugins to shape the EQ of their tracks.
All DAWs will come with at least one stock EQ plugin (for example, FL Studio’s famous “Parametric EQ 2”). Alternatively, there are many incredible third-party EQ plugins out there to choose from.
Simply add an EQ plugin to your chosen sound, and from there you can shape the frequency response of the sound. This could include adding some high-end frequencies to make the sound more bright and “crisp”, or boosting the bass frequencies to add power and “body” to the sound.
Like I said, you can do this by adjusting the gain at specific points along a frequency spectrum. To illustrate this, let’s take a look at a few EQ examples.
EQ in Music – How to use an EQ plugin
To demonstrate a standard EQ plugin, I’ll be using FabFilter’s incredible “Pro-Q 3” plugin. This is easily one of the most popular, comprehensive EQ plugins on the market, and has a simple, intuitive interface.
Without adding any EQ to the sound, the interface looks like this:
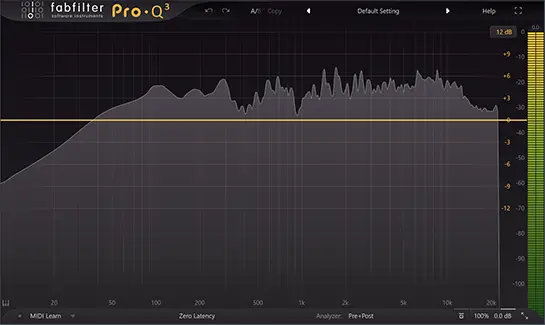
The Spectrum Analyzer
The lower, highlighted section is the frequency spectrum, shown within the spectrum analyzer.
The Spectrum Analyzer functions like an X-Y Graph. The bottom X-axis displays the frequencies (low-end, bass frequencies on the left, high-end frequencies towards the right). The Y-axis shows the Amplitude (gain) of the frequency response.
I’d highly recommend getting started with an EQ plugin with a spectrum analyzer, as it it much more intuitive for beginners.
To give a very basic example, here is an EQ curve added to the low-end/mid frequencies at 70 hZ:
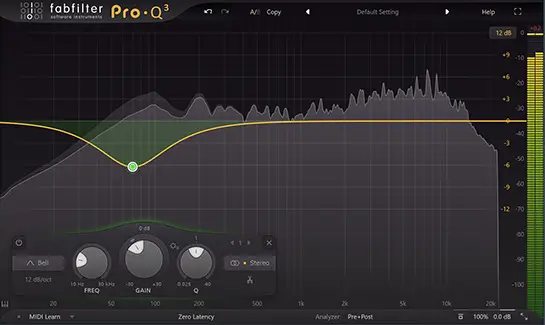
This is a simple bell-curve that is attenuating (reducing the gain) of the frequencies at the 70 hZ point of the frequency spectrum.
So what effect will this have? This EQ treatment will remove some of the low-end of the sound, decreasing the bass frequencies while retaining the mid / high-end frequency ranges.
Of course, with any EQ plugin you can add more than one EQ “point”. Take a look at the EQ pattern below which involves multiple EQ points to reduce specific low-end frequencies and boost the high-end of the sound.
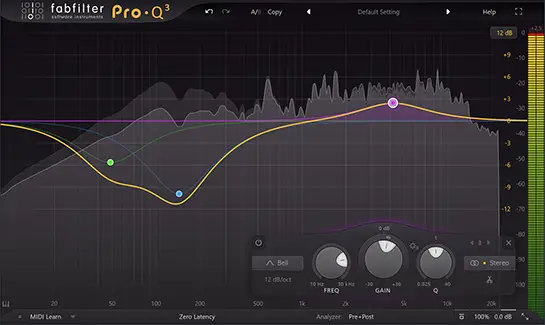
EQ curves
There are several types of EQ curves that can be used to finetune your EQ treatment. The most common shapes found in almost all EQs are Bell, High/Low Shelf, High/Low Pass, and Bandpass.
• Bell – As the name suggests, this EQ curve forms a “bell” shape. This is great for pinpointing certain frequency ranges to either boost or attenuate.
• High/Low Shelf – This can be used to boost/attenuate the frequencies below or above a certain point. It doesn’t remove the frequencies entirely, creating a “shelf”-like appearance.
• High/Low Pass – This can be used to completely remove the frequencies above or below a certain frequency value. A high-pass filter removes all frequencies below a chosen point, and a low-pass filter removes all frequencies above a chosen point.
• Bandpass – This filter type cuts frequencies below AND above certain points, creating a “band” of frequencies that remain.
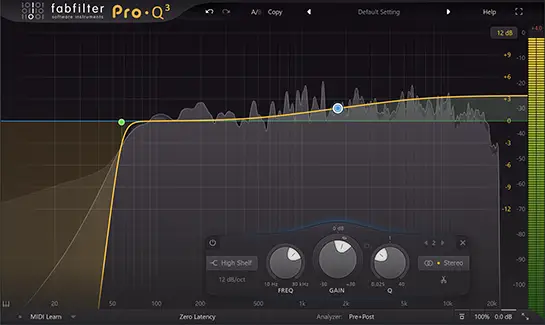
What is EQ in music – Frequency / Gain / Q
There are three main controls you’ll need to understand when using an EQ plugin: frequency, gain and Q value.
• Frequency – The frequency is your chosen “point” on the frequency spectrum you’d like to edit. Remember, lower frequencies (20 hZ – 500 hZ) represent the bass of your sounds, while higher frequencies (7.5 kHz +) reflect the bright, high-end part of the sound.
• Gain – Once you’ve chosen your frequency value, the gain determines how this frequency is affected. This is the amount that your EQ point is boosted or attenuated by. For example, if you added 12 dB gain to a certain frequency, this would dramatically increase the gain at that frequency.
• Q – This controls the shape of the EQ curve. High Q values means a steeper EQ curve, which affects a smaller range, allowing you to pinpoint specific frequencies. Lower Q values affect a broader range of frequencies and tend to have a more subtle, gentle effect.
Using EQ to mix your tracks
EQ is a crucial part of the mixing process, and if done correctly can breathe life into an otherwise dull, thin-sounding track.
However, it’s also a mixing tool that trips up a lot of beginners. If a track is poorly EQ’d, it can completely ruin the vibe and atmosphere of the final mix.
Therefore, it’s important that you get your head around the basic concepts of EQ, and begin applying these concepts to your own tracks. If you’re a beginner, mixing in general is a skill that requires time, patience and dedication, it is NOT something you can master overnight.
If you’re interested in learning some EQ tips and tricks for beginners, why not check out some of our guides below:
• 5 EQ Tips for Beginners to TRANSFORM Your Mixes (2022)
• The 8 Best EQ VST Plugins on the Market (2022)
• 5 Biggest Mixing Mistakes and How to Fix Them (2022 Music Mixing Tips)
• Top 10 Mixing Tips that will TRANSFORM your Final Track